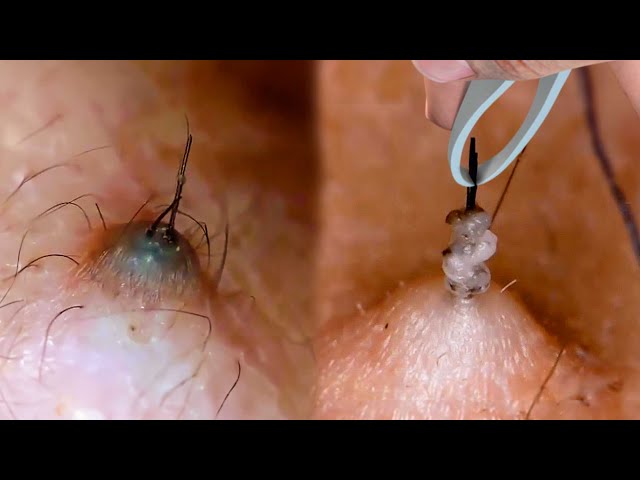
An ingrown hair describes a hair that curls back or grows sideways into the skin, causing pain, redness, and swelling. Ingrown hairs form when dead skin cells block hair follicles, trapping hairs beneath the skin's surface.
Ingrown hairs are a common skin condition, particularly in areas with coarse or curly hair. Shaving, waxing, and tight clothing can increase the risk of developing ingrown hairs. Proper hair removal techniques and exfoliation can help prevent and treat ingrown hairs. Alexander Monro first described ingrown hairs in 1783, laying the foundation for understanding and managing this condition.
This article delves into the causes, prevention, and treatment options for ingrown hairs, providing comprehensive information for individuals seeking to address this common skin issue.
How Do Ingrown Hairs Form
Understanding the factors that contribute to ingrown hair formation is essential for effective prevention and treatment. Key aspects to consider include:
- Shaving technique
- Hair type
- Skin exfoliation
- Inflammation
- Hygiene practices
Shaving against the grain, using dull razors, or applying excessive pressure can irritate the skin and increase the likelihood of ingrown hairs. Coarse or curly hair is more prone to ingrowing, as it tends to curl back more easily. Regular exfoliation removes dead skin cells that can clog hair follicles. Inflammation, caused by factors such as tight clothing or skin conditions, can also contribute to ingrown hair formation. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as keeping the skin clean and dry, helps prevent bacterial infections that can worsen ingrown hairs.
Shaving technique
Shaving technique plays a critical role in the formation of ingrown hairs. When hair is shaved against the grain, the sharp edge of the razor can cut the hair below the skin's surface. The hair may then grow back into the skin, leading to an ingrown hair. Shaving with a dull razor can also increase the risk of ingrown hairs, as it can cause the hair to break off unevenly, making it more likely to curl back into the skin.
Using excessive pressure while shaving can also irritate the skin and increase the likelihood of ingrown hairs. When too much pressure is applied, the razor can cut the hair too close to the skin, increasing the chances of the hair growing back into the skin.
Understanding the connection between shaving technique and ingrown hair formation is essential for preventing this common skin condition. By shaving with the grain, using a sharp razor, and applying gentle pressure, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing ingrown hairs.
Hair type
Hair type plays a significant role in the formation of ingrown hairs. Coarse and curly hair is more likely to become ingrown than fine and straight hair. This is because coarse and curly hair tends to be thicker and more prone to curling back into the skin. Additionally, curly hair may be more difficult to shave or remove, which can increase the risk of ingrown hairs. For example, individuals with naturally thick, curly hair may experience a higher incidence of ingrown hairs after shaving their legs or facial hair.
The shape and texture of hair follicles can also affect the likelihood of ingrown hair formation. Follicles that are curved or irregularly shaped are more likely to trap hairs, leading to ingrown hairs. Additionally, hair that grows in multiple directions can increase the risk of ingrown hairs, as it is more likely to come into contact with the skin and curl back in.
Understanding the connection between hair type and ingrown hair formation is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Individuals with coarse, curly, or thick hair may need to take extra care when shaving or removing hair to minimize the risk of ingrown hairs. Using sharp razors, shaving with the grain, and exfoliating regularly can help prevent ingrown hairs in individuals with all hair types.
Skin exfoliation
Skin exfoliation plays a crucial role in preventing ingrown hairs by removing dead skin cells that can clog hair follicles. When dead skin cells accumulate on the skin's surface, they can block the hair follicle opening, preventing the hair shaft from emerging properly. As the hair continues to grow, it may curl back into the skin, resulting in an ingrown hair.
Regular exfoliation helps to slough away dead skin cells, unclogging hair follicles and reducing the risk of ingrown hairs. Exfoliation can be achieved through various methods, including physical exfoliation with scrubs or brushes, chemical exfoliation with products containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs), and enzymatic exfoliation with products containing enzymes like bromelain or papain.
In addition to preventing ingrown hairs, exfoliation offers numerous other benefits for the skin. It helps to improve skin texture and radiance, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and promote the absorption of skincare products. Regular exfoliation is recommended for all skin types, but it is especially beneficial for individuals with acne-prone skin or those who experience frequent ingrown hairs.
Understanding the connection between skin exfoliation and ingrown hair formation is essential for maintaining healthy, ingrown hair-free skin. By incorporating regular exfoliation into their skincare routine, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing ingrown hairs and enjoy the numerous other benefits that exfoliation offers.
Inflammation
Inflammation plays a significant role in the formation of ingrown hairs. When the skin is inflamed, it produces a variety of chemicals that can damage hair follicles and promote ingrown hair development. These chemicals can also cause the skin to become thicker and more difficult for hair to penetrate, further increasing the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Immune response: When the skin is injured, the immune system releases chemicals that trigger inflammation. These chemicals can damage hair follicles and make them more likely to produce ingrown hairs.
- Bacterial infection: Bacteria can enter the hair follicle and cause an infection, which leads to inflammation. The inflammation can damage the hair follicle and make it more likely to produce ingrown hairs.
- Skin irritation: Skin irritation from shaving, waxing, or other hair removal methods can cause inflammation. The inflammation can damage hair follicles and make them more likely to produce ingrown hairs.
- Underlying skin conditions: Some underlying skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, can cause inflammation that can lead to ingrown hairs.
Understanding the role of inflammation in ingrown hair formation is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By reducing inflammation, individuals can reduce their risk of developing ingrown hairs and improve the overall health of their skin.
Hygiene practices
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial for preventing ingrown hairs. Bacteria and dirt can accumulate on the skin's surface, clog hair follicles, and create a favorable environment for ingrown hairs to develop. Regular cleansing of the skin helps remove bacteria, dirt, and dead skin cells, reducing the risk of ingrown hairs.
For example, individuals who do not shower regularly are more likely to develop ingrown hairs in areas such as the underarms, groin, and buttocks. These areas are prone to sweating and accumulation of bacteria, which can clog hair follicles and lead to ingrown hairs. Similarly, individuals who wear tight clothing for extended periods may experience ingrown hairs due to friction and moisture buildup, which can create a breeding ground for bacteria.
Understanding the connection between hygiene practices and ingrown hair formation is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. By maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regular cleansing, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and avoiding sharing personal items like razors and towels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing ingrown hairs.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section addresses common questions and clarifies aspects related to the formation of ingrown hairs.
Question 1: What causes ingrown hairs?
Answer: Ingrown hairs form when dead skin cells block hair follicles, causing hair to curl back or grow sideways into the skin.
Question 2: Who is more prone to ingrown hairs?
Answer: Individuals with coarse or curly hair, as well as those who shave or wax frequently, are more likely to develop ingrown hairs.
Question 3: How can I prevent ingrown hairs?
Answer: Exfoliate regularly, shave with the grain, use a sharp razor, and avoid wearing tight clothing to reduce the risk of ingrown hairs.
Question 4: What are the signs and symptoms of ingrown hairs?
Answer: Ingrown hairs appear as small, red bumps that may be painful, itchy, or inflamed.
Question 5: How can I treat ingrown hairs?
Answer: Mild ingrown hairs can be treated with warm compresses, exfoliation, or over-the-counter antiseptic creams. Severe ingrown hairs may require professional extraction.
Question 6: Can ingrown hairs lead to complications?
Answer: In rare cases, ingrown hairs can become infected and lead to scarring or other skin problems.
These FAQs provide essential insights into the formation, prevention, and treatment of ingrown hairs. Understanding these factors can help individuals effectively manage this common skin condition.
For further discussion on related skin concerns, refer to the following section on managing skin irritation and preventing infections.
Tips for Preventing and Treating Ingrown Hairs
This section provides practical tips for preventing and treating ingrown hairs, helping individuals maintain smooth, healthy skin.
Tip 1: Exfoliate Regularly: Use a gentle scrub or brush to remove dead skin cells and unclog hair follicles, reducing the risk of ingrown hairs.
Tip 2: Shave with the Grain: Avoid shaving against the direction of hair growth, as this increases the chances of hairs curling back into the skin.
Tip 3: Use a Sharp Razor: Dull razors can tug at hairs and cause them to break, making them more likely to become ingrown.
Tip 4: Avoid Tight Clothing: Tight clothing can create friction and irritation, increasing the risk of ingrown hairs.
Tip 5: Keep Skin Clean: Wash the affected area regularly with a mild soap to remove bacteria and prevent infection.
Tip 6: Use Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to ingrown hairs can help soften the skin and reduce inflammation.
Tip 7: Over-the-Counter Medications: Topical creams or gels containing antibiotics or antiseptic agents can help prevent or treat bacterial infections associated with ingrown hairs.
Tip 8: Seek Professional Help: If ingrown hairs become severe or infected, consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for proper treatment.
By following these tips, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing ingrown hairs and enjoy smoother, healthier skin. These measures can help prevent hair follicles from becoming clogged, reduce inflammation, and promote optimal skin health.
In the concluding section, we will delve into the importance of maintaining good skincare habits and seeking professional advice when necessary to keep ingrown hairs under control and ensure healthy, radiant skin.
Conclusion
This article has explored the intricate factors that contribute to the formation of ingrown hairs, providing valuable insights for understanding and addressing this common skin condition. Key takeaways include the significant role of hair type, shaving technique, skin exfoliation, inflammation, and hygiene practices in the development of ingrown hairs. These factors are interconnected, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment.
Maintaining good skincare habits, including regular exfoliation, proper shaving techniques, and avoiding tight clothing, can significantly reduce the risk of ingrown hairs. Additionally, seeking early professional advice from dermatologists or healthcare professionals can ensure timely treatment, preventing complications and promoting healthy skin. Understanding the causes and mechanisms of ingrown hair formation empowers individuals to take proactive measures and achieve smoother, more radiant skin.

No comments:
Post a Comment